Tuesday, 24 March 2020
Deploying Your Application to Amazon EKS with GitHub Actions and Weave Flux
Last month I've published a tutorial to show you how to build and push a docker image to Amazon ECR with GitHub Actions.
However, if you are using Amazon EKS, you may need to manually update the image URI every time you have a new release. is there a way to automate the whole process that the image URI can be updated automatically? Yes. Here's the solution for you.
Flux is the operator that makes GitOps happen in your cluster. It ensures that the cluster config matches the one in git and automates your deployments.
Suppose you've already provisioned your Amazon EKS cluster. If not, please check out my previous post.
Configure your kubectl so that you can connect to an Amazon EKS cluster by running
```bash
export AWS_REGION="ap-southeast-1"
export CLUSTER_NAME="your-cluster-name"
aws eks --region ${AWS_REGION} update-kubeconfig --name ${CLUSTER_NAME}
```
If you enable load balancer ingress access, make sure that you have the corresponding IAM role.
```bash
aws iam get-role --role-name "AWSServiceRoleForElasticLoadBalancing" || aws iam create-service-linked-role --aws-service-name "elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com"
```
Run your manifest files
```bash
kubectl apply -f manifests/deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f manifests/service.yaml
kubectl apply -f manifests/ingress.yaml
```
A sample deployment can be found [here](https://github.com/github-developer/example-actions-flux-eks/blob/master/manifests/deployment.yml). Make sure you have ``fluxcd.io/automated: "true"`` under ``annotations``.
The next step is to run Flux on our EKS cluster. Let's create a new namespace ``flux`` in where flux objects will be installed.
```bash
kubectl create ns flux
```
Install flux objects under ``flux`` namespace. By doing so, flux is monitoring the manifests folder for the changes.
```bash
export GHUSER=your-github-user
export GHREPO=your-github-repo
fluxctl install \
--git-user=${GHUSER} \
--git-email=${GHUSER}@users.noreply.github.com \
--git-url=git@github.com:${GHUSER}/${GHREPO} \
--git-path=manifests \
--namespace=flux | kubectl apply -f -
```
You should see the following
```bash
serviceaccount/flux created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flux unchanged
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flux configured
deployment.apps/flux created
secret/flux-git-deploy created
deployment.apps/memcached created
service/memcached created
```
Let's verify if they are running or not
```bash
kubectl get all -n flux
```
```bash
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/flux-6449c6bd94-7gz88 1/1 Running 0 5m
pod/memcached-86869f57fd-52cwn 1/1 Running 0 5m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/memcached ClusterIP 10.100.152.74 11211/TCP 5m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/flux 1/1 1 1 5m
deployment.apps/memcached 1/1 1 1 5m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/flux-6449c6bd94 1 1 0 5m
replicaset.apps/memcached-86869f57fd 1 1 1 5m
```
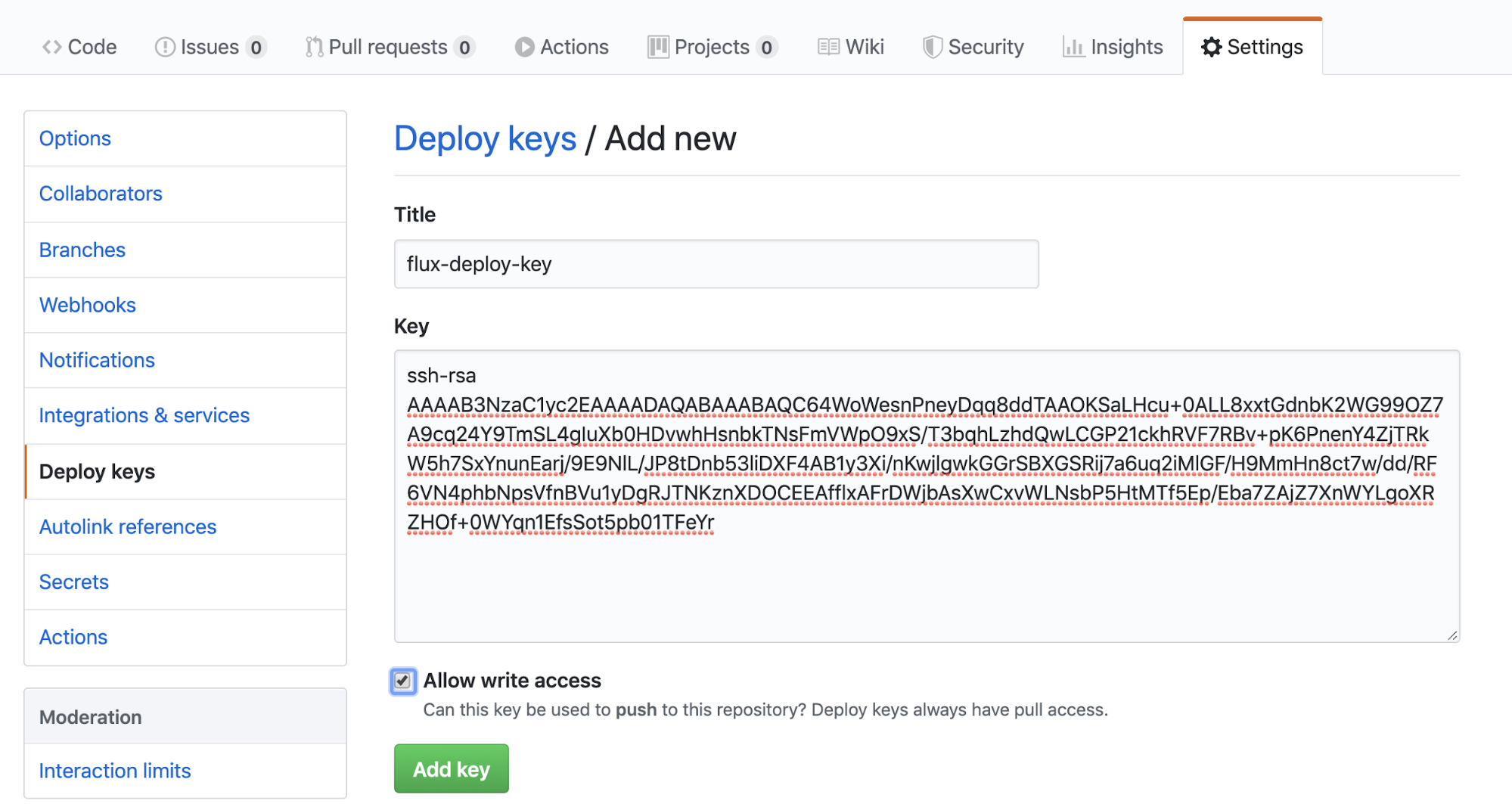
Upon the completion of deployment, the docker image URI in deployment.yaml should be updated. To do so, we need to grand read/write access to the repository with a deploy key so that Flux can be able to write it back every time it deploys.
By running
```bash
fluxctl identity --k8s-fwd-ns flux
```
You should get a deploy key.
```bash
ssh-rsa
AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQC64WoWesnPneyDqq8ddTAAOKSaLHcu+0ALL8xxtGdnbK2WG99OZ7A9cq24Y9TmSL4gIuXb0HDvwhHsnbkTNsFmVWpO9xS/T3bqhLzhdQwLCGP21ckhRVF7RBv+pK6PnenY4ZjTRkW5h7SxYnunEarj/9E9NlL/JP8tDnb53liDXF4AB1y3Xi/nKwjlgwkGGrSBXGSRij7a6uq2iMlGF/H9MmHn8ct7w/dd/RF6VN4phbNpsVfnBVu1yDgRJTNKznXDOCEEAfflxAFrDWjbAsXwCxvWLNsbP5HtMTf5Ep/Eba7ZAjZ7XnWYLgoXRZHOf+0WYqn1EfsSot5pb01TFeYr
```
Go to Settings > Deploy keys and click 'Add deploy key'
Enter the title and the key you just generated. Make sure you tick 'Allow write access'
Then we can go back to the console and run the following command to sync Flux and Github.
```bash
fluxctl sync --k8s-fwd-ns flux
```
For the first time, you should see
```bash
Synchronizing with git@github.com:wingkwong/eks-flux-playground
Revision of master to apply is a8e3b45
Waiting for a8e3b45 to be applied ...
Done.
```
If you make a change and push to master, Github Actions helps to build and push the docker image to Amazon ECR, and Flux helps to deploy the latest image to Amazon EKS.
Go back to the repository, you should see there is a new commit on your deployment.yaml while the change is only updating the image URI.
```bash
Auto-release xxxxxxxxxxxx.dkr.ecr.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/eks-flux…
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
A Fun Problem - Math
# Problem Statement JATC's math teacher always gives the class some interesting math problems so that they don't get bored. Today t...
-
SHA stands for Secure Hashing Algorithm and 2 is just a version number. SHA-2 revises the construction and the big-length of the signature f...
-
## SQRT Decomposition Square Root Decomposition is an technique optimizating common operations in time complexity O(sqrt(N)). The idea of t...
No comments:
Post a Comment