Wednesday, 29 January 2020
Forwarding Port Traffic in Kubernete
Supposing you've migrated your services to kubernetes and there is a service with a hardcoded port 8755 from your legacy application listing some products in a JSON format a where the requirement declares the standard port is 80. To address this problem, you can use the ambassador design to export access to the service on port 80.
First of all, create a ConfigMap definition, pipe the configuration to ``haproxy.cfg`` and save it as ``my-service-ambassador-config.yml``
```
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: my-service-ambassador-config
data:
haproxy.cfg: |-
global
daemon
maxconn 256
defaults
mode http
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
listen http-in
bind *:80
server server1 127.0.0.1:8775 maxconn 32
```
```
kubectl apply -f my-service-ambassador-config.yml
```
Create a pod definition called ``my-service.yml``. As you can see, there is an ambassador container running the ``haproxy:1.7`` image and proxying the incoming traffic on port 80 to the legacy service on port 8775.
```
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
containers:
- name: legacy-service
image: legacy-service:1
- name: haproxy-ambassador
image: haproxy:1.7
ports:
- containerPort: 80
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /usr/local/etc/haproxy
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: my-service-ambassador-config
```
```
kubectl apply -f my-service.yml
```
Let's test it by creating a busybox pod
```
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: busybox
spec:
containers:
- name: myapp-container
image: radial/busyboxplus:curl
command: ['sh', '-c', 'while true; do sleep 3600; done']
```
```
kubectl apply -f busybox.yml
```
The sub-command ``$(kubectl get pod my-service -o=custom-columns=IP:.status.podIP --no-headers)`` is used to get the IP address of ``my-service``.
```
kubectl exec busybox -- curl $(kubectl get pod my-service -o=custom-columns=IP:.status.podIP --no-headers):80
```
For more about ambassador pattern, please check out [Design patterns for container-based distributed systems](https://static.googleusercontent.com/media/research.google.com/en//pubs/archive/45406.pdf)
Tuesday, 28 January 2020
How to fix Insufficient pods issue when deploying to Amazon EKS?
Recently I tried to deploy a nodeJS application to Amazon EKS and found that the deployment was not ready and the pod was stuck at Pending state indefinitely. I had no idea what's happening.
In order to troubleshoot, I increased kubectl output verbosity to ``--v=9``. For more: [Kubectl output verbosity and debugging](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/cheatsheet/#kubectl-output-verbosity-and-debugging).
To get more details, I ran ``kubectl describe pod`` and got the below message:
```
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Warning FailedScheduling 17s (x14 over 18m) default-scheduler 0/1 nodes are available: 1 Insufficient pods.
```
I was wondering the maximum number of pods per each node, so I ran
```
kubectl get nodes -o yaml | grep pods
```
It returned
```
4
```
Then, I wanted to know how many pods which were currently running.
```
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces | grep Running | wc -l
```
I also got
```
4
```
From [Architecting Kubernetes clusters — choosing a worker node size](https://learnk8s.io/kubernetes-node-size), we know the below info:
```
On Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS),
the maximum number of pods per node depends on the node type and ranges from 4 to 737.
On Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE),
the limit is 100 pods per node, regardless of the type of node.
On Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS),
the default limit is 30 pods per node but it can be increased up to 250.
```
As more pods need to be provisioned, the maximum number of pods are not enough in this case. As I was just working on a demonstration, so I chose a small node type ``t2.micro`` to minimise the cost.
How to increase this value? This is calculated from [AWS ENI documentation](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/using-eni.html#AvailableIpPerENI). The formula is
```
N * (M-1) + 2
```
where
```
N is the number of Elastic Network Interfaces (ENI) of the instance type
M is the number of IP addresses of a single ENI
```
So I was using ``t2.micro``, the calculation is ``2 * (2-1) + 2 = 4``.
AWS also provides a mapping file [here](https://github.com/awslabs/amazon-eks-ami/blob/master/files/eni-max-pods.txt) so that you don't need to calculate yourself.
The final solution is to change the node type from ``t2.micro`` to ``t3.small`` in my case.
Monday, 27 January 2020
How to push a Docker image to Amazon ECR
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) is a fully-managed Docker container registry that makes it easy for developers to store, manage, and deploy Docker container images.
In this article, you'll learn how to push your docker image to Amazon ECR.
Build your docker application
```
docker build -t hello-world .
```
Run the following command to see the image
```
docker image ls
```
```
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
hello-world latest 3b521a2b570b 6 minutes ago 26MB
```
Before moving to the next step, make sure you have setup your aws credentials. To do that, you can run ``aws configure`` to perform your setup. The region for this demostration is ``ap-southeast-1``.
After the configuration setup, you can run the below command to verify
```
aws sts get-caller-identity
```
Retrieve the login command to use to authenticate your Docker client to your registry
```
aws ecr get-login --no-include-email --region ap-southeast-1
```
Your Docker client must authenticate before pushing and pulling images. Copy the command and run it. You should see the below message
```
Login Succeeded
```
Create an ECR repository
```
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name hello-world --region ap-southeast-1
```
```json
{
"repository": {
"repositoryArn": "arn:aws:ecr:ap-southeast-1:473625259682:repository/hello-world",
"registryId": "473625259682",
"repositoryName": "hello-world",
"repositoryUri": "473625259682.dkr.ecr.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/hello-world",
"createdAt": 1576506790.0,
"imageTagMutability": "MUTABLE"
}
}
```
Tag your image
```
docker tag hello-world:latest 473625259682.dkr.ecr.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/hello-world:latest
```
Push the image to the repository you just created
```
docker push 473625259682.dkr.ecr.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/hello-world:latest
```
That's it. You've successfully push your image to the ECR. In the next part, you'll learn how to simplify your development to production workflow with [Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)](https://aws.amazon.com/ecs/).
For more about ECR, please check out the user guide [here](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECR/latest/userguide/what-is-ecr.html).
Wednesday, 22 January 2020
7 Strategies for Migrating Applications to AWS
This post outlines seven common strategies for migration: "The 7 R's".
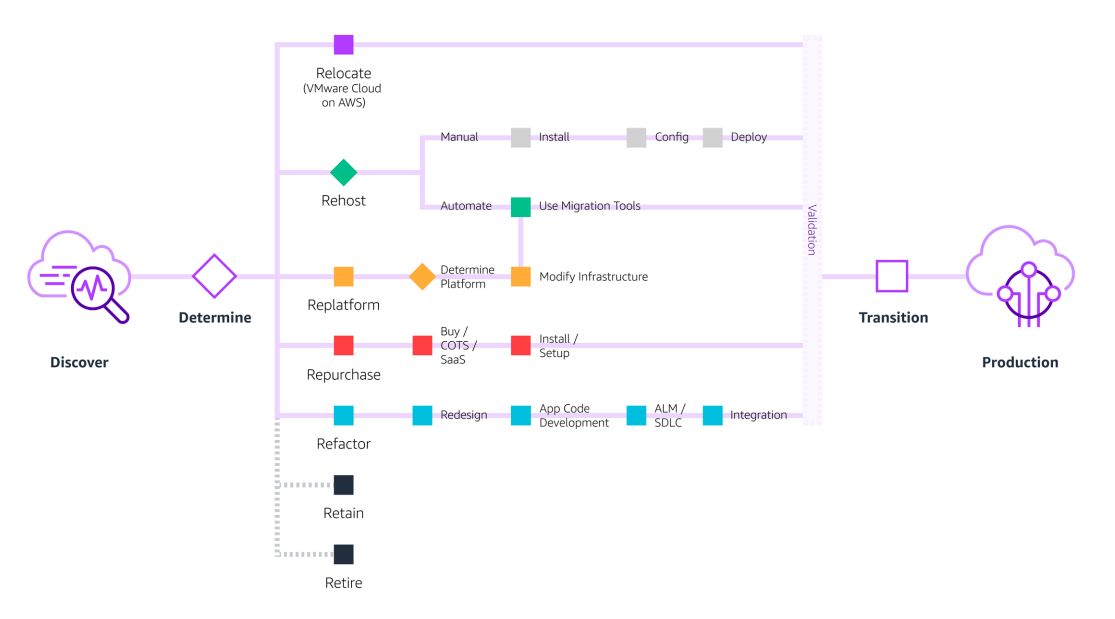
# 1. Relocate
> Move vSphere-based applications to AWS without application changes
VMware Cloud on AWS allows you to quickly relocate hundreds of applications virtualised on vSphere to the AWS Cloud in just days and to maintain consistent operations with your VMware Cloud Foundation-based environments.
Once in the AWS Cloud, your applications are easier to optimise or rearchitect to take advantage of the breadth and depth of AWS services
# 2. Rehost
> Also known as “lift-and-shift”
In a large-scale migration scenario where you need to migrate and scale
quickly to meet a business case, such as a data centre lease termination, we find that the majority of applications are rehosted.
Most rehosting can be automated with tools such as CloudEndure Migration,
(from CloudEndure, an AWS company). CloudEndure Migration quickly rehosts
a large number of machines from multiple source platforms (physical, virtual, or another cloud) to AWS without worrying about compatibility, performance disruption, long cutover windows, or long-distance data replications. For times when you can’t install an agent on the server, AWS Server Migration Service offers an agentless service, which makes it easier and faster for you to migrate thousands of on-premises workloads to AWS from a snapshot of the existing servers.
We find that applications are easier to optimise and re-architect once they are already running in the cloud, as your organisation will have developed better skills and can iteratively adopt new technologies (e.g., containers, serverless, etc.) without having to deploy and manage the underlying services.
# 3. Replatform
> Sometimes referred to as “lift-tinker-and-shift”
This entails making a few cloud optimisations in order to achieve tangible benefits, without changing the core architecture of the application. For example, if you’re managing a messaging broker today, you can easily replace this with the fully managed Amazon MQ service, without re-writing your applications or paying for third-party software licenses. Or, if you’re migrating a Windows-based application that requires file storage, you can use the fully-managed Amazon FSx for Windows
File Server. To reduce the amount of time you spend managing database instances, you can move to a database-as-a-service offering such as Amazon Relational Database Service. AWS Database Migration Service makes this re-platforming easier than ever. When moving from one database source or version to a new platform or software version, AWS Database Migration Service keeps the source database fully operational during the migration, enabling near-zero downtime during the cutover.
# 4. Repurchase
> Replace your current environment, casually referred to as “drop and shop”
This is a decision to move to a newer version of the software or purchase an entirely new solution. You may also be looking for a new software licensing model that allows you more flexibility to match your business needs. AWS Marketplace is a curated digital catalog where you can find, buy, deploy, and manage third-party software and services that you need to build solutions and run your business.
# 5. Refactor
> Change the way the application is architected and developed, usually
done by employing cloud-native features
Typically, refactoring (or rearchitecting) is driven by a strong business need to add features, scale, or improve performance that would otherwise be difficult to achieve in the application’s existing environment.
If your organisation is looking to boost agility or improve business continuity by moving to a service-oriented architecture (SOA), this strategy may be worth pursuing—even though it is often the most expensive solution.
# 6. Retain
> Do nothing, for now
You may have portions of your IT portfolio that you are not ready to migrate, or believe are best-kept on-premises. Keep in mind that as more of your portfolio moves to the cloud, allocation of data centre expenses across fewer applications may eventually drive a need to revisit the retained applications.
For applications that remain on-premises, AWS Outposts bring the same hardware and software in the AWS cloud, the same services and APIs, the same management tools, and the same support and operating model to virtually any data centre, co-location space, or on-premises facility. With Outposts, you have a truly consistent hybrid cloud, so that you can develop once and deploy across Outposts on-premises or in the AWS cloud without having to recertify your applications.
# 7. Retire
> Decommission or archive unneeded portions of your IT portfolio
By rationalising your IT portfolio and identifying assets that are no longer useful and can be turned off, you can boost your business case and direct your team’s attention toward maintaining the resources that are more widely used.
Wednesday, 15 January 2020
How did AWS Improve VPC Networking for Lambda to Address Cold Start Problem
I believe there are a lot of people facing a cold start problem when they use Lambda to request resources in their own VPCs like Amazon RDS or Redis. Lambda function is managed by AWS. You can access anything on the public Internet. However, when your lambda function is configured to connect to your own VPC, it needs an elastic network interface (ENI) in VPC to allow the communication to your private resources. Normally creating and attaching a new ENI takes several seconds. However, if your Lambda environment scales to handle huge request spikes, you need more ENIs. The time causes long cold starts before it can be invoked. Some potential issues may include reaching ENI limit in your account or hitting API rate limit on creating ENIs.

About months ago, AWS leveraged AWS Hyperplane, which is a netwwork function virtualization platform used for network load balancer and NAT gateway, to allow inter-VPC connectivity by providing NAT capabilities. When you deploy your Lambda, it will help you to build a VPC-to-VPC NAT in AWS Lambda Service VPC and the required ENIs in your own VPC. By doing so, the time can be significantly dropped from 10 seconds to 1 second or even few milliseconds.

Let's create a quick test using AWS CDK.
Here we create a lambda function first with inline code
```javascript
const fn = new lambda.Function(this, 'LambdaFunc', {
code: new lambda.InlineCode(`exports.handler = (event, context, callback) =>
callback(null, {
statusCode: '200',
body: JSON.stringify(event),
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
});`),
handler: 'index.handler',
runtime: lambda.Runtime.NODEJS_8_10,
});
```
Define an API Gateway REST API with the Lambda function declared above
```javascript
new apigateway.LambdaRestApi(this, 'RestAPI', {
handler: fn,
endpointTypes: [apigateway.EndpointType.REGIONAL]
});
```
After deploying the stack, you will see the endpoint in the output. By running ``time curl -s ``, you should see the time taken is less than 1 second.
Monday, 13 January 2020
Autoscaling an EKS Cluster with Cluster Autoscaler
Last time we introduced how to use ``eksctl`` to create an EKS cluster. If you miss the previous post, please check out [Creating an EKS Cluster in AWS Using eksctl](https://dev.to/wingkwong/creating-an-eks-cluster-in-aws-using-eksctl-10ik). In this article, you will learn how to autoscale an EKS cluster using a default Kubernetes component - [Cluster Autoscaler](https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/tree/master/cluster-autoscaler). It can be used to scale either pods or nodes in a cluster and automatically increases the size of an auto-scaling group.
Go to AWS console and navigate to EC2 Dashboard - Auto Scaling Groups.
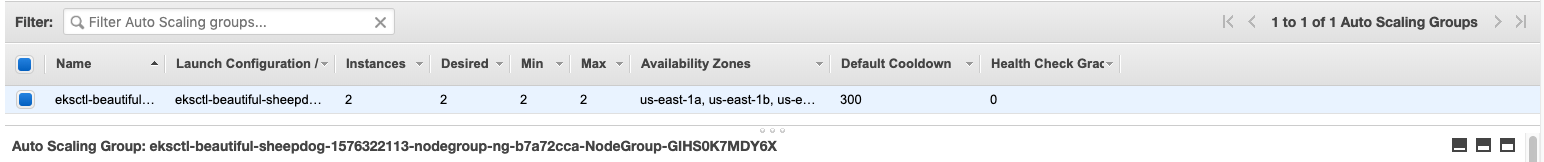
Copy the auto-scaling group name and replace ```` with it.
With ``--nodes=2:8``, it will auto-scale with minimum 2 nodes and maximum 8 nodes.
cluster_autoscaler.yaml
```
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events","endpoints"]
verbs: ["create", "patch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/eviction"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/status"]
verbs: ["update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
resourceNames: ["cluster-autoscaler"]
verbs: ["get","update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get","update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods","services","replicationcontrollers","persistentvolumeclaims","persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["replicasets","daemonsets"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get"]
- apiGroups: ["policy"]
resources: ["poddisruptionbudgets"]
verbs: ["watch","list"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["statefulsets"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["cluster-autoscaler-status"]
verbs: ["delete","get","update"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-autoscaler
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: cluster-autoscaler
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
labels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
spec:
serviceAccountName: cluster-autoscaler
containers:
- image: k8s.gcr.io/cluster-autoscaler:v1.2.2
name: cluster-autoscaler
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 300Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 300Mi
command:
- ./cluster-autoscaler
- --v=4
- --stderrthreshold=info
- --cloud-provider=aws
- --skip-nodes-with-local-storage=false
- --nodes=2:8:
env:
- name: AWS_REGION
value: us-east-1
volumeMounts:
- name: ssl-certs
mountPath: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
readOnly: true
imagePullPolicy: "Always"
volumes:
- name: ssl-certs
hostPath:
path: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt"
```
Then we need to apply below inline IAM policy to worker nodes to allow them to manipulate auto-scaling
```json
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups",
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingInstances",
"autoscaling:DescribeTags",
"autoscaling:SetDesiredCapacity",
"autoscaling:TerminateInstanceInAutoScalingGroup"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
```
Go back to AWS Console - IAM and search the worker node group role created by eksctl
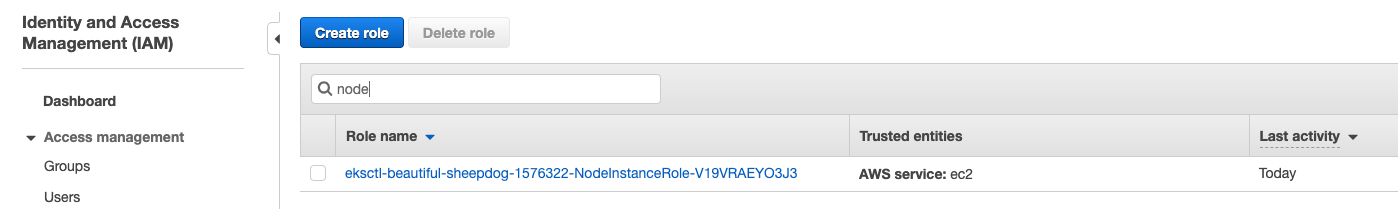
Click Add inline poilcy
Click JSON tab and paste the above policy
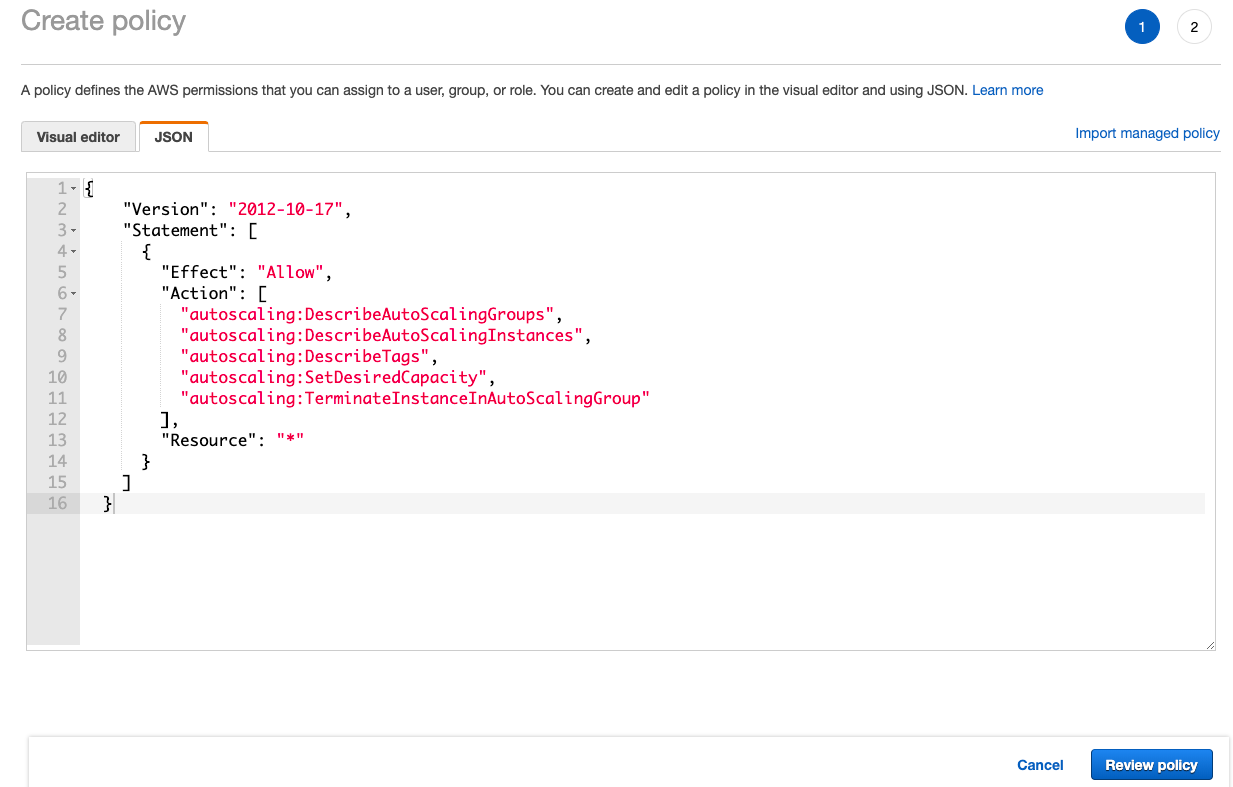
Name the policy and click Create policy
Run ``kubectl apply`` to deploy the autoscaler
```
kubectl apply -f cluster_autoscaler.yaml
```
You should see the following
```
serviceaccount/cluster-autoscaler created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler created
deployment.extensions/cluster-autoscaler created
```
Then let's deploy an Nginx sample application
```
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-scaleout
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
service: nginx
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx-scaleout
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
```
```
kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
```
Check the deployment
```
kubectl get deployment/nginx-scaleout
```
```
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-scaleout 1/1 1 1 14s
```
Let's scale the deployment with 10 replicas
```
kubectl scale --replicas=10 deployment/nginx-scaleout
```
```
deployment.extensions/nginx-scaleout scaled
```
You can run the following to see how it goes
```
kubectl logs -f deployment/cluster-autoscaler -n kube-system
```
Let's run it again
```
kubectl get deployment/nginx-scaleout
```
You can see 10 replicas have been scaled out
```
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-scaleout 10/10 10 10 5m
```
Go to AWS Console - EC2 Dashboard. You should see there are 2 more instances spinning up.
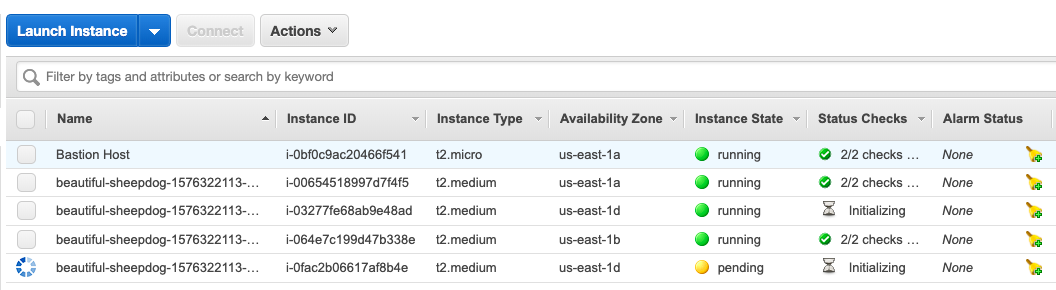
After a few minutes, try to see the nodes
```
kubectl get nodes
```
You'll get two more nodes joining to the cluster.
```
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-28-185.ec2.internal Ready 174m v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
ip-192-168-33-53.ec2.internal Ready 174m v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
ip-192-168-64-112.ec2.internal Ready 87s v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
ip-192-168-90-156.ec2.internal Ready 2m5s v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
```
To delete the deployments, run the following commands
```
kubectl delete -f cluster_autoscaler.yaml
kubectl delete -f nginx.yaml
```
Friday, 10 January 2020
Creating an EKS Cluster in AWS Using eksctl
In this article, we will create an EKS Cluster in AWS using [eksctl](https://github.com/weaveworks/eksctl).
eksctl is a simple CLI tool for creating clusters on EKS - Amazon's new managed Kubernetes service for EC2. It is written in Go, and uses CloudFormation.
This is the general architecture. This article only focuses on EKS part.
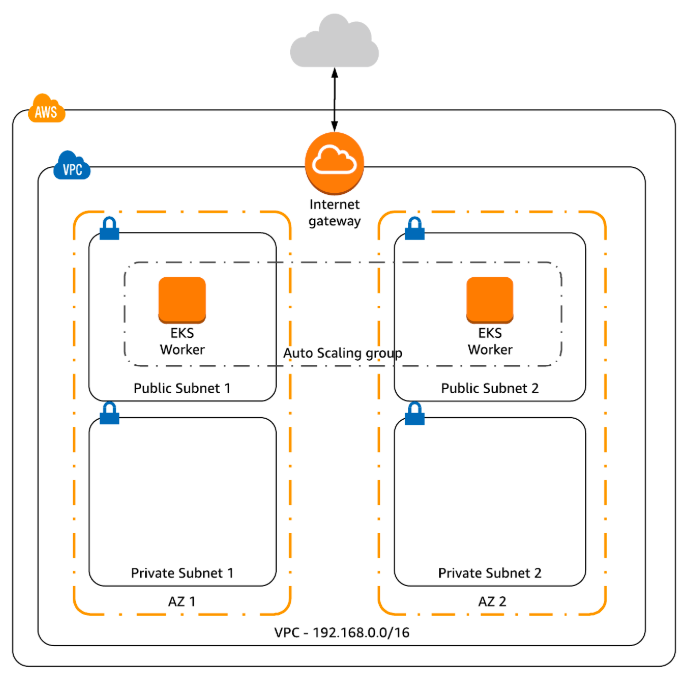
To install eksctl, you can use [homebrew](https://brew.sh/) if you are a macOS user:
```bash
brew tap weaveworks/tap
brew install weaveworks/tap/eksctl
```
or use [chocolatey](https://chocolatey.org/) if you are a Windows user:
```bash
chocolatey install eksctl
```
Before creating a cluster, make sure you have setup your aws credentials. To do that, you can run ``aws configure`` to perform your setup. The region for this demostration is ``us-east-1``.
After the configuration setup, you can run the below command to verify
```bash
aws sts get-caller-identity
```
To create a EKS cluster, you can simply use
```bash
eksctl create cluster
```
or with some parameters
```bash
eksctl create cluster --region=us-east-1 --node-type=t2.medium
```
If you don't specify parameters, the default parameters will be used:
```
exciting auto-generated name, e.g. "fabulous-mushroom-1527688624"
2x m5.large nodes (this instance type suits most common use-cases, and is good value for money)
use official AWS EKS AMI
us-west-2 region
dedicated VPC (check your quotas)
using static AMI resolver
```
The process may take up to 15 minutes.
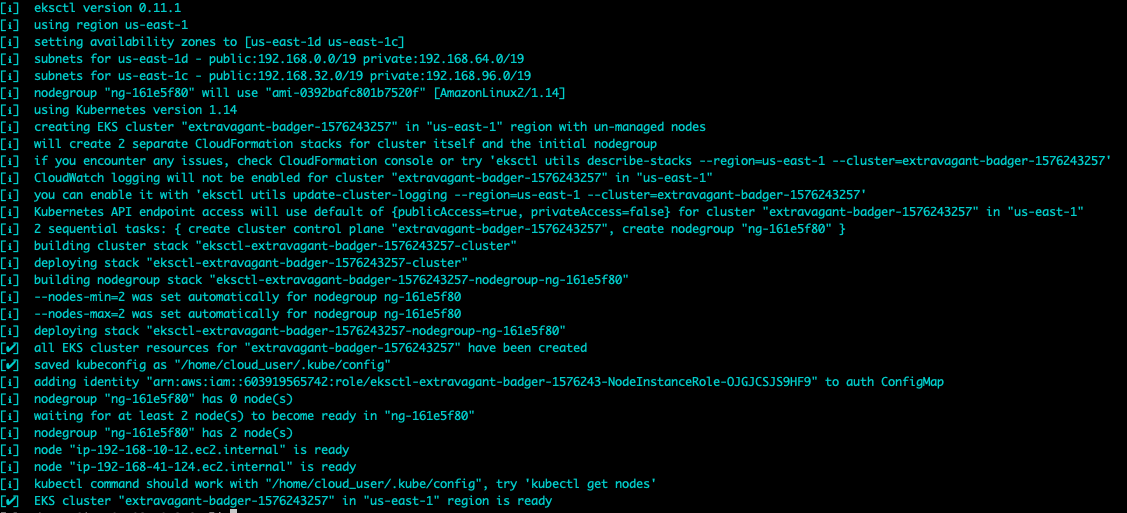
Once it is ready, run the following command to verify
```bash
kubectl get nodes
```
```
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-10-12.ec2.internal Ready 2m6s v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
ip-192-168-41-124.ec2.internal Ready 2m5s v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
```
If you go to AWS Console and direct to EKS page, you can see there are three clusters created by ``eksctl``. Since we do not specify the name, so the cluster name is generated randomly.
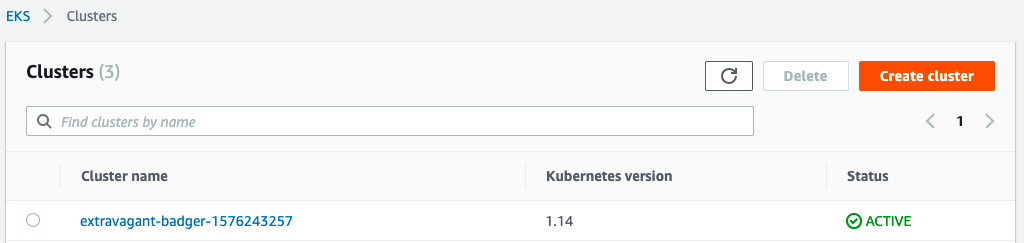
For the eksctl documentation, please check out [here](https://eksctl.io/).
Wednesday, 8 January 2020
Fixing Wrong Prompt String on a EC2 Linux Instance
One of my colleagues reported that he could not run a npm command on a EC2 instance (Amazon Linux AMI 2018.03). When I connected to the EC2 instance via SSH and found that the prompt string was using the default one which is ``\s-\v\$``. It shows the basename of the shell process with the version.
The ``~/.bashrc`` file looks normal. ``~/.bashrc`` should execute ``/etc/bashrc`` where ``PROMPT_COMMAND`` will be set based on the environment variable ``TERM`` after login.
```bash
# Source global definitions
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
```
As I am using Mac OSX Terminal, my ``TERM`` is ``xterm-256color``, which matches the first case. ``/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm`` does not exist, hence my ``PROMPT_COMMAND`` would be ``printf "\033]0;%s@%s:%s\007" "${USER}" "${HOSTNAME%%.*}" "${PWD/#$HOME/~}"``
```bash
if [ -z "$PROMPT_COMMAND" ]; then
case $TERM in
xterm*)
if [ -e /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND=/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm
else
PROMPT_COMMAND='printf "\033]0;%s@%s:%s\007" "${USER}" "${HOSTNAME%%.*}" "${PWD/#$HOME/~}"'
fi
;;
screen)
if [ -e /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-screen ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND=/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-screen
else
PROMPT_COMMAND='printf "\033]0;%s@%s:%s\033\\" "${USER}" "${HOSTNAME%%.*}" "${PWD/#$HOME/~}"'
fi
;;
*)
[ -e /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-default ] && PROMPT_COMMAND=/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-default
;;
esac
fi
```
When an interactive shell is invoked, it executes commands from ``/etc/profile``, ``~/.bash_profile``, ``~/.bash_login``, and ``~/.profile``. The last three files does not exist.
``~/.bashrc`` is executed when the interactive shell is not a login shell. Hence, I added the following lines to ``~/.profile`` as it is executed by the command interpreter for login shell.
```bash
if [ -n "$BASH_VERSION" ]; then
if [ -f "$HOME/.bashrc" ]; then
. "$HOME/.bashrc"
fi
fi
```
Restart the shell and test. It is back to normal now and $PS1 is back to ``[\u@\h \W]\$``
```
[ec2-user@ip-xxx-xx-xx-xxx ~]$
```
Sunday, 5 January 2020
Docker Commands Cheat Sheet
docker build with a tag
```
docker build -t wingkwong/example:latest .
```
Run a simple container using the hello-world image:
```
docker run hello-world
```
Run a container using a specific image tag:
```
docker run nginx:1.15.11
```
Run a container with a command and arguments:
```
docker run busybox echo hello world!
```
Run an Nginx container customized with a variety of flags:
- -d: Run container in detached mode. The **docker run** command will exit immediately and the container will run in the background
- --name: A container is assigned a random name by default, but you can give it a more descriptive name with this flag
- --restart: specify when the container should be automatically restarted
- no(default): never restart the container
- on-failure: only if the container fails (exits with a non-zero exit code)
- always: always restart the container whether it succeeds or fails. Also starts the container automatically on daemon startup
- unless-stopped: always restart the container whether it succeeds or fails, and on daemon startup, unless the container was manually stopped
```
docker run -d --name nginx --restart unless-stopped -p 8080:80 --memory 500M --memory-reservation 256M nginx
```
List any currently running containers:
```
docker ps
```
List all containers, both running and stopped:
```
docker ps -a
```
Stop the Nginx container:
```
docker container stop nginx
```
Start a stopped container:
```
docker container start nginx
```
Delete a container (but it must be stopped first):
```
docker container rm nginx
```
Downgrade to a previous version:
```
sudo systemctl stop docker
sudo apt-get remove -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce=5:18.09.4~3-0~ubuntu-bionic docker-ce-cli=5:18.09.4~3-0~ubuntu-bionic
docker version
```
Upgrade to a new version:
```
sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce=5:18.09.5~3-0~ubuntu-bionic docker-ce-cli=5:18.09.5~3-0~ubuntu-bionic
docker version
```
Check the current default logging driver:
```
docker info | grep Logging
```
Edit daemon.json to set a new default logging driver configuration:
```
sudo vi /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "15m"
}
}
```
Restart docker
```
sudo systemctl restart docker
```
Run a docker container, overriding the system default logging driver settings:
```
docker run --log-driver json-file --log-opt max-size=50m nginx
```
Install Docker Engine:
```
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get -y install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg-agent \
software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88
sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable"
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce=5:18.09.5~3-0~ubuntu-bionic docker-ce-cli=5:18.09.5~3-0~ubuntu-bionic containerd.io
sudo usermod -a -G docker cloud_user
```
Initialize Docker Swarm
```
docker swarm init --advertise-addr
```
View the current state of the swarm:
```
docker info
```
List the current nodes in the swarm and their status:
```
docker node ls
```
Get a join token from the manager. Run this command on the swarm manager:
```
docker swarm join-token worker
```
Copy the docker swarm join command provided in the output and run it on both workers:
```
docker swarm join --token :2377
```
Docker Swarm Backup (on manager)
```
sudo systemctl stop docker
sudo tar -zvcf backup.tar.gz -C /var/lib/docker/swarm
sudo systemctl start docker
```
Docker Swarm Restore (on manager)
```
sudo systemctl stop docker
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker/swarm/*
sudo tar -zxvf backup.tar.gz -C /var/lib/docker/swarm/
sudo systemctl start docker
docker node ls
```
View file system layes in an image. Nginx as an example
```
docker image history nginx
```
Delete an iamge. Nginx as an example
```
docker image rm nginx:1.14.0
```
Download an image
```
docker image pull nginx:1.14.0
```
List images on the system:
```
docker image ls
docker image ls -a
```
Force Deleteion of an image used by a container
```
docker run -d --name nginx nginx:1.14.0
docker image rm -f nginx:1.14.0
```
Delete an iamge. Nginx as an example
```
docker image rm nginx:1.14.0
```
Locate a dangling image and clean it up. Nginx as an example
```
docker image ls -a
docker container ls
docker container rm -f nginx
docker image ls -a
docker image prune
```
Inspect image metadata. Nginx as an example
```
docker image inspect nginx:1.14.0
docker image inspect nginx:1.14.0 --format "{{.Architecture}}"
docker image inspect nginx:1.14.0 --format "{{.Architecture}} {{.Os}}"
```
Enable Docker Swarm autolock
```
docker swarm update --autolock=true
```
Unlock the swarm using the unlock key
```
docker swarm unlock
```
Get the current unlock key
```
docker swarm unlock-key
```
Rotate the unlock key
```
docker swarm unlock-key -rotate
```
Disable autolock
```
docker swarm update --autolock=false
```
Start Compose application with detached mode:
```
docker-compose up -d
```
Stop Compose application
```
docker-compose down
```
List the Docker Compose container
```
docker-compose ps
```
Deploy a new Stack to the cluster using a compose file
```
docker stack deploy -c
```
List current stacks
```
docker stack ls
```
List the tasks associated with a stack
```
docker stack ps
```
List the services associated with a stack
```
docker stack services
```
Delete a stack
```
docker stack rm
```
Thursday, 2 January 2020
Generating an S3 Presigned URL in Go
When you create an object in s3, by default it is private. If you access an object url, you should see
```
Access Denied
0E7531544D92C793
wCC8lVp1Yqnjl2ItHuFxhAKCr2IWLziOavoWyif/Spn1WVsHUyTHEK3vckTK49Kmy/M/YIHQvQ4=
```
If you need to share the object to other people without making it public, you can control the access using a fine-grained IAM policy or use presigned url to grant your users temporary access to a specific object.
In this post, you will learn how to generate a s3 presigned url in Go.
First, let's import some packages that will be used
```
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go/aws"
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go/aws/session"
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go/service/s3"
"time"
)
```
Create a function which takes three parameters - bucket, key and region. It returns the presigned url at the end.
```
func GetS3PresignedUrl(bucket string, key string, region string, expiration time.Duration) string{
// TODO
}
```
Initialize a session in the target region that the SDK will use to load credentials from the shared credentials file ``~/.aws/credentials``.
```
sess, err := session.NewSession(&aws.Config{
Region: aws.String(region)},
)
```
Create S3 service client
```
svc := s3.New(sess)
```
Construct a new GetObjectRequest
```
req, _ := svc.GetObjectRequest(&s3.GetObjectInput{
Bucket: aws.String(bucket),
Key: aws.String(key),
})
```
Create a presigned url with expiration time
```
presignedUrl, err := req.Presign(expiration * time.Minute)
```
Check if it can be presigned or not
```
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Failed to sign request", err)
}
```
Return the presigned URL
```go
return presignedUrl
```
You can find the complete code [here](https://gist.github.com/wingkwong/a7a33fee0b640997991753d9f06ff120)
Let's have a quick test
```
S3PresignedUrl.GetS3PresignedUrl("test-s3-presigned-url-s2kvn2bs", "d4fb43054862c768921504199c78958b.jpg", "ap-southeast-1", 15)
```
The ``presignedUrl`` is
```
https://test-s3-presigned-url-s2kvn2bs.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/d4fb43054862c768921504199c78958b.jpg?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Credential=AKIAW4RRUVRQTI2J564J%2F20191227%2Fap-southeast-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20191227T055220Z&X-Amz-Expires=900&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&X-Amz-Signature=ed1d94edd580976f0175eca1c4c1944a9f215fd572540e3e3c7ed1c317656358
```
If we break it down, the presigned url contains ``X-Amz-Algorithm``, ``X-Amz-Credential``, ``X-Amz-Date``, ``X-Amz-Expires`` and ``X-Amz-Signature``. These are AWS Signature Version 4 query parameters.
```
https://test-s3-presigned-url-s2kvn2bs.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/d4fb43054862c768921504199c78958b.jpg
?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256
&X-Amz-Credential=AKIAW4RRUVRQTI2J564J%2F20191227%2Fap-southeast-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request
&X-Amz-Date=20191227T055220Z
&X-Amz-Expires=900&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host
&X-Amz-Signature=ed1d94edd580976f0175eca1c4c1944a9f215fd572540e3e3c7ed1c317656358
```
Browse the presigned url
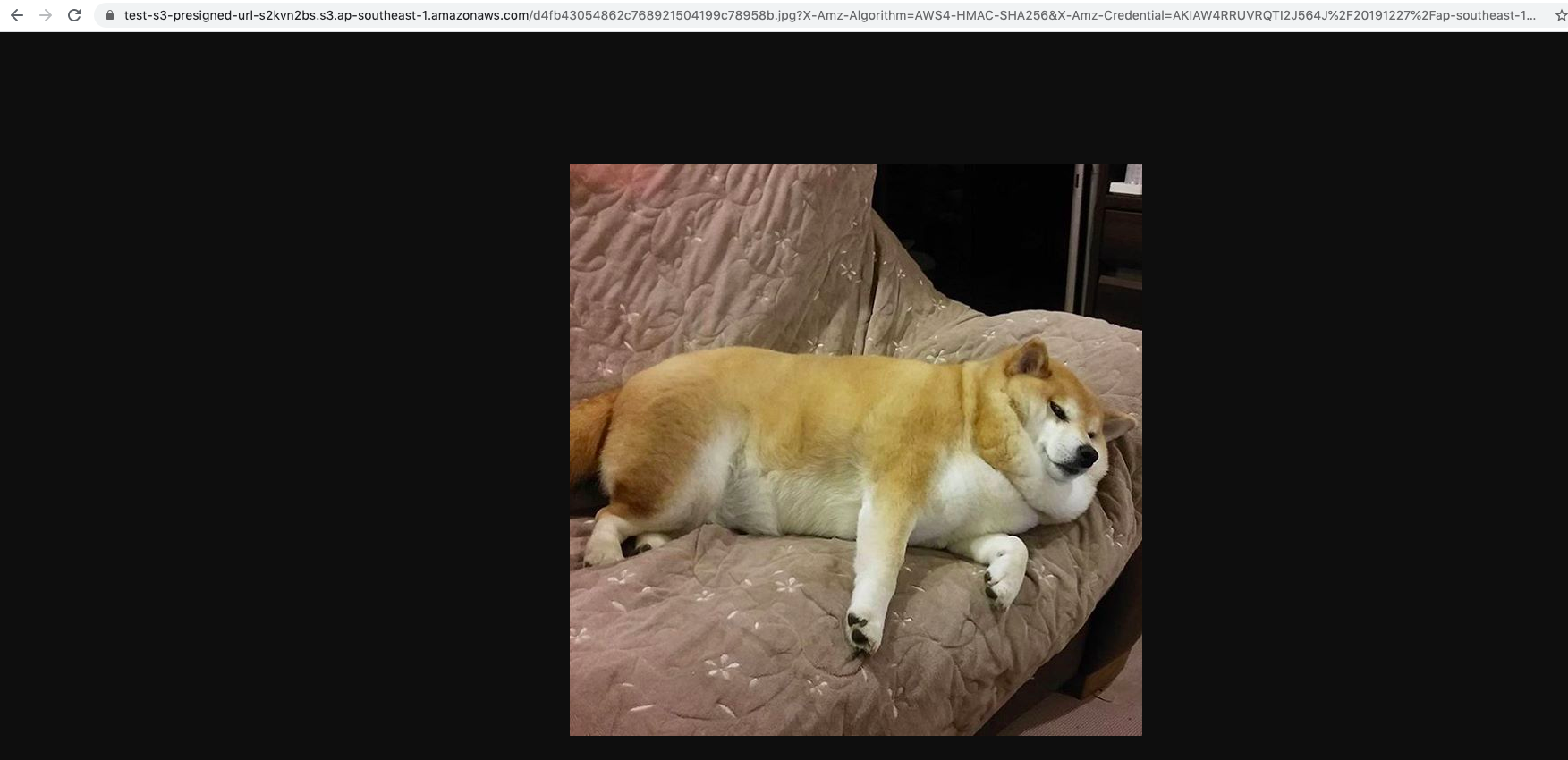
After the expiration time, you will see the below message
```
Request has expired
900
2019-12-27T06:07:20Z
2019-12-27T07:13:10Z
805E5BD14FFAEA84
My9ZyJNtcixWAu91g79KVomutCU2AE4cj8G2eQo4KERAm/AoRxzppIZfXs5Cw+cuhuyo8eFgtvY=
```
Complete Code: [https://gist.github.com/wingkwong/a7a33fee0b640997991753d9f06ff120](https://gist.github.com/wingkwong/a7a33fee0b640997991753d9f06ff120)
AccessDenied
AccessDenied
Make Good
You can practice the problem [here](https://codeforces.com/contest/1270/problem/C).
## Problem
An array a[0], a[1], ... , a[n - 1] of nonnegative integer numbers is said to be good if
```
a[0] + a[1] + ... + a[n - 1] = 2 * (a[0] ^ a[1] ^ ... ^ a[n - 1])
```
Given that an array of length n, append at most 3 elements to it to make it good.
## Solution
Let S be the sum of the array, which is a[0] + a[1] + ... + a[n - 1] and X be their XOR value. Then we'll have
```
S = 2 * X
```
A simple solution here is to add X and X + S to the array.
```
S = 2 * X
S + X + (X + S) = 2 * (X ^ X ^ (X + S)) // X ^ X = 0
2 * (X + S) = 2 * (X + S)
```
C++ Implementation
```
ll S = 0, X = 0;
REP(i, n) {
ll a; cin >> a;
S += a;
X ^= b;
}
cout << 2 << "\n";
cout << X << " " << X + S << "\n";
```
Wednesday, 1 January 2020
Copying Files from On-Premises to Azure Storage Accounts using AzCopy
In this tutorial, you will learn how to copy data using AzCopy
- From an on-premise to the Azure Storage Account
- From Azure Storage Account to another Azure Storage Account
- From the Azure Storage Account to an on-premise
# What is AzCopy
AzCopy is a command-line utility that you can use to copy blobs or files to or from a storage account.
# Disable Security Configuration
If you are using Virtual Machine, you need to change the security configuration in order to download AzCopy.
Login to your Virtual Machine and Open Server Manager
On the left navigation, click Local Server
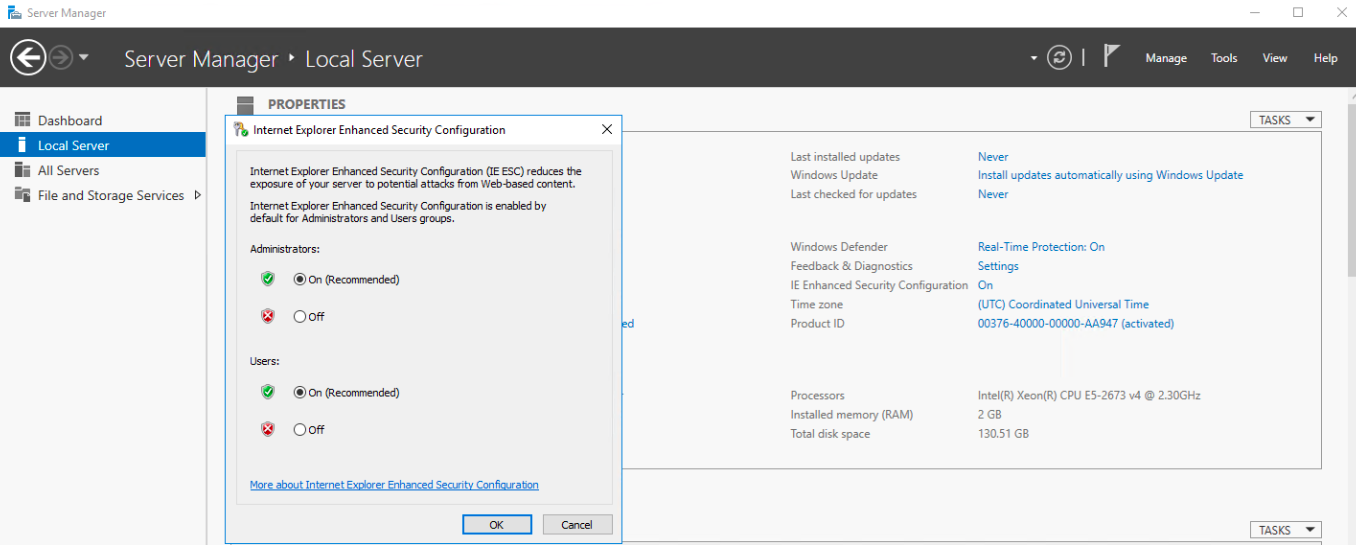
Click On next to IE Enhanced Security Configuration.
For Administrators, select Off and click OK.
# Download AzCopy
Now we can download AzCopy.
Open the browser and browse https://aka.ms/downloadazcopy
Click Run

Click Next
Tick I accept the terms in the License Agreement and click Next
Select a destination folder and click Next
Click Install
# Create Storage Account
> A storage account provides a unique namespace in Azure for your data. Every object that you store in Azure Storage has an address that includes your unique account name. The combination of the account name and the Azure Storage blob endpoint forms the base address for the objects in your storage account.
Go to Azure Portal and select Storage Accounts
Click Add
Select a Resource group if it is not populated. Enter the storage account name you want to use and leave other options as default. Click Review and Create.
Click Create
Wait for the deployment. It may takes around 30 seconds or longer.
Once it's complete, click Go to Resource
# Create Blob Service Container
We will use Azure Blob storage for storing our data for this demonstration.
> Azure Blob storage is Microsoft's object storage solution for the cloud. Blob storage is optimised for storing massive amounts of unstructured data. Unstructured data is data that doesn't adhere to a particular data model or definition, such as text or binary data.
Under Blob service, click Containers.
> A container organises a set of blobs, similar to a directory in a file system. A storage account can include an unlimited number of containers, and a container can store an unlimited number of blobs.
Create a new Container. Enter the name and click ok
Now let's do the above steps again to create our second Storage Account.
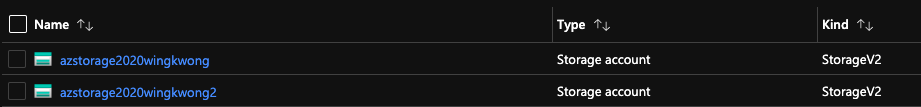
Now we got two Storage Accounts.
# Copy data from an on-premise to Storage Account 1
Go to Storage Account 1, Navigate back to Blob service - Containers. Click the three dot button and click Container properties
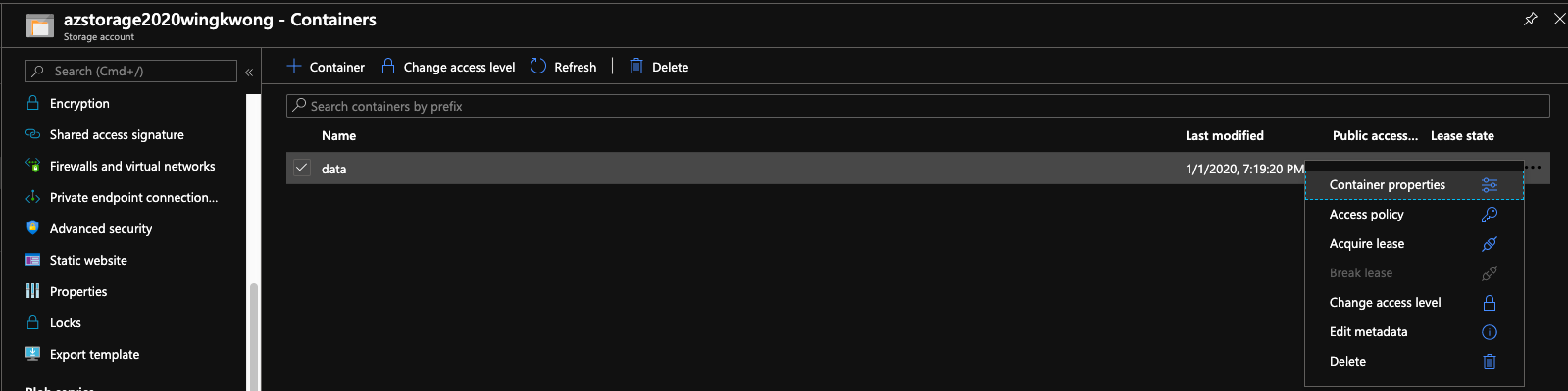
Copy the URL and paste it to a text editor first. We'll use it later.
Since the container is private, we need to access it with the container access key.
Under Settings, you can see ``Access keys``. Copy ``Key`` from key1.
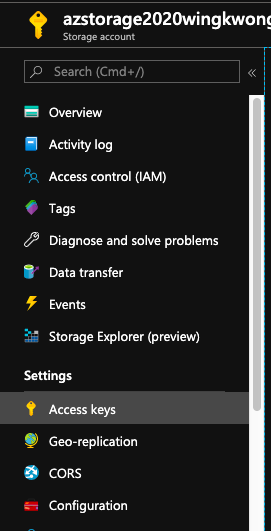
You may wonder why there are two access keys. It is designed for avoiding downtime and for temporary sharing of access keys. For more, please check out [Why does an Azure storage account have two access keys?](https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/mast/2013/11/06/why-does-an-azure-storage-account-have-two-access-keys/)
Go back to Virtual Machine, launch Command Prompt and type the below command and click Enter. Remember to replace and with the values you just copied.
For this demonstration, we're going to upload files under ``C:\Windows\System32\drivers``
```
azcopy
/Source:C:\Windows\System32\drivers
/Dest:
/DestKey:
```
You should see similar output
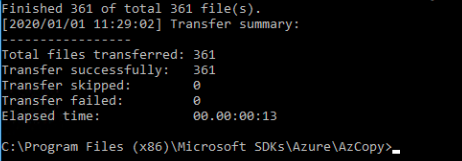
Back to the console, click Storage Explorer(preview). Under BLOB CONTAINERS, click ``data``. You should see the files that you just uploaded using AzCopy.
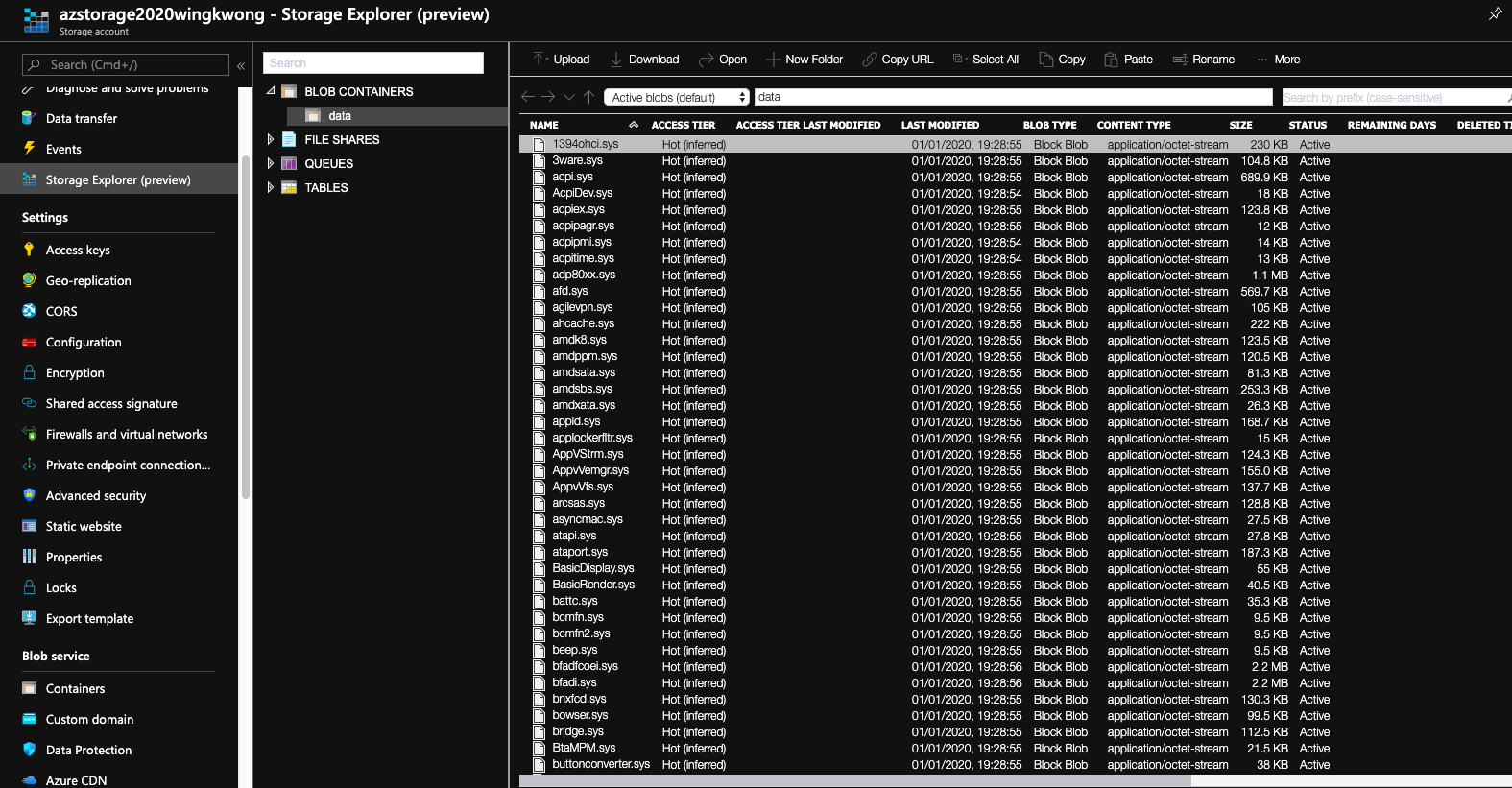
# Copy data from Storage Account 1 to Storage Account 2
What if you want to copy files from one blob container in a Storage Account to that in another Storage Account?
Similarly, copy the source URL in the second Storage Account.
Go back to Command Prompt,
```
azcopy
/source:
/Dest:
/sourcekey:
/DestKey
/s
```
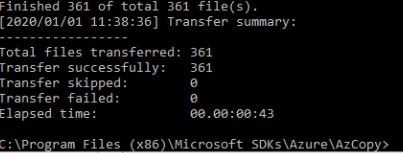
Go back to the console, check Storage Explorer in Storage Account 2.
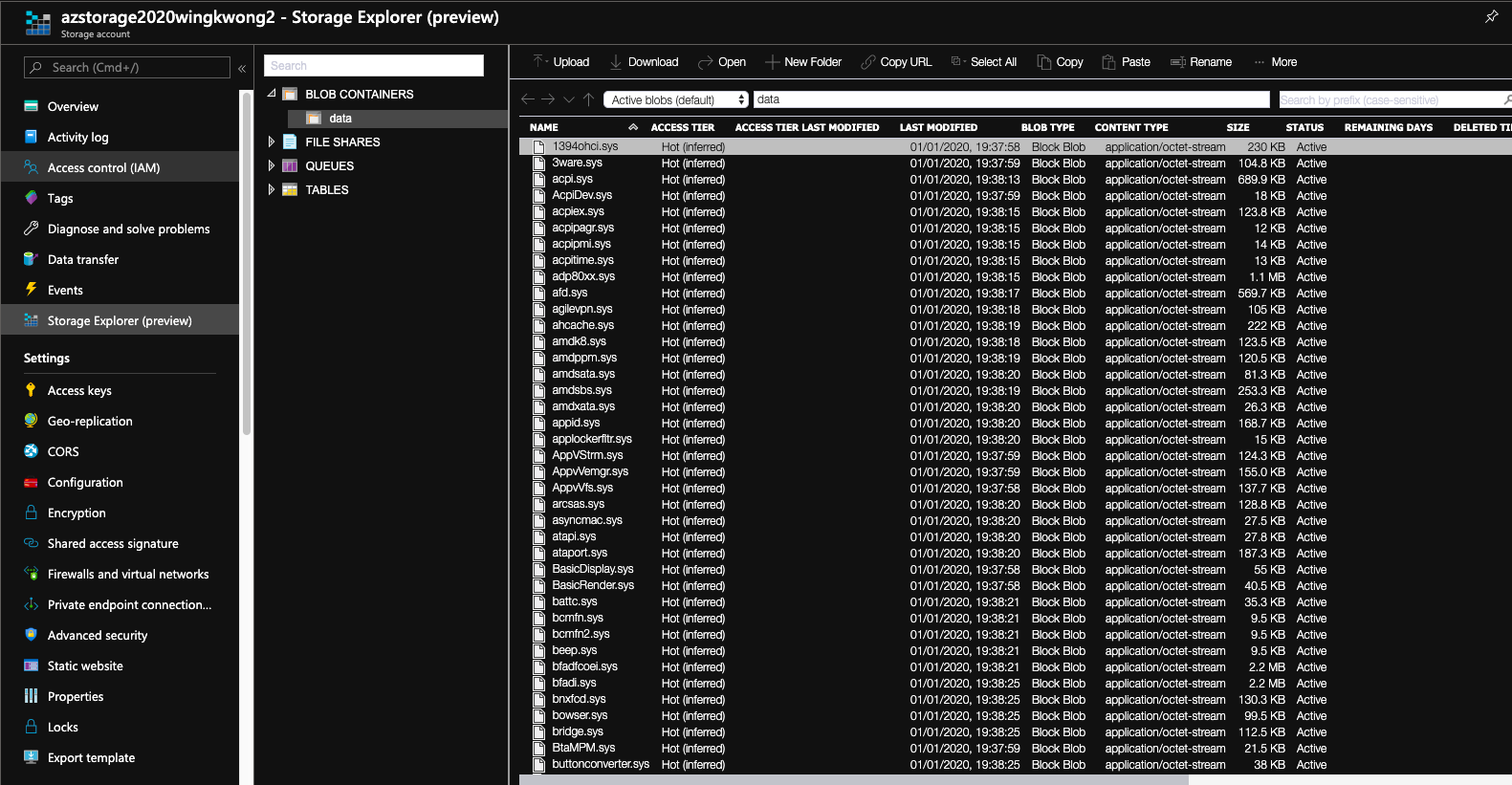
We've successfully copied the files from Storage Account 1 to Storage Account 2.
# Copy data from Storage Account to an on-premise
What if we want to copy the files from Storage Account to our local system? You may already know the answer.
```
azcopy
/source:
/Dest
/SourceKey:
/s
```
That's it.
Creating an ALB from the AWS CLI
In this article, we will create an application load balancer from the command line interface.
**Scenario:**
We would have an ALB serving a single point of contact for clients with two listeners forwarding traffic to target groups with health check.
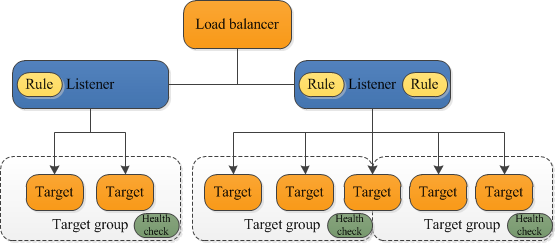
**Prerequisites:**
- awscli has been installed
- two EC2 instances are configured
- instance 1:
- default VPC
- subnet: us-east-1a
- auto-assign public IP: enable
- instance 2:
- default VPC
- subnet: us-east-1b
- auto-assign public IP: enable
First, login in to the admin instance using ssh
```bash
ssh @
```
Once you are in, configure your aws settings.
```bash
aws configure
```
Fill in the following values:
```
AWS Access Key ID [None]:
AWS Secret Access Key [None]:
Default region name [None]: us-east-1
Default output format [None]:
```
Supposing your instances are in default VPC
```bash
aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filters "Name=isDefault, Values=true"
```
Once you get the ID of VPC, use the follwoing command to get subnet IDs:
```bash
aws ec2 describe-subnets --filters "Name=vpc-id,Values=" --query 'Subnets[*].{ID:SubnetId}'
```
To get security group ID:
aws ec2 describe-security-groups --filter Name=vpc-id,Values= Name=group-name,Values=
Then enter the following command and replace and
```bash
aws elbv2 create-load-balancer --name alblab-load-balancer --subnets --security-groups
```
An ALB is created. The next step is to create a target group.
```bash
aws elbv2 create-target-group --name demo-targets --protocol HTTP --port 80 --vpc-id
```
Copy ``TargetGroupArn`` which will be used later
Then, register the targets
```bash
aws elbv2 register-targets --target-group-arn --targets Id= Id=
```
For the instance IDs, you can use ``aws ec2 describe-instances`` to get them.
Then, enter the following command to create a listener:
```bash
aws elbv2 create-listener --load-balancer-arn --protocol HTTP --port 80 --default-actions Type=forward TargetGroupArn=
```
Perform a health check with the following command:
```bash
aws elbv2 describe-target-health --target-group-arn
```
At this moment, the status of the instances is unhealthy. It is because we still need to configure out instances as web servers.
Log in to instance 1 using ssh and run the following commands:
```bash
sudo yum update -y
sudo yum install -y httpd
sudo service httpd start
sudo chkconfig httpd on
```
If you copy the public IP address and paste it into a browser. You should see the Apache test page. If not, that means your ingress on the instance's security group is incorrect. It should allow HTTP on port 80.
If you copy the DNS name and paste it into a browser, you should see the Apache test page.
However, if we take a look at the target groups. We will see the instanecs are unhealthy. The health check for the ALB is checking the return code of 200, but currently there is no ``index.html`` page for the instances to return the 200 code to the ALB.
Let's create one.
```bash
cd /var/www/html
sudo touch index.html
sudo chmod 777 index.html
vi index.html
```
Add something to index.html
Save and exit by pressing Esc and typing
```bash
:wq
```
Then we do the same thing for instance 2.
Once you have done, go back to admin instance.
Verify the target health check
```bash
aws elbv2 describe-target-health --target-group-arn
```
You should be see "OK" message.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
A Fun Problem - Math
# Problem Statement JATC's math teacher always gives the class some interesting math problems so that they don't get bored. Today t...
-
SHA stands for Secure Hashing Algorithm and 2 is just a version number. SHA-2 revises the construction and the big-length of the signature f...
-
## SQRT Decomposition Square Root Decomposition is an technique optimizating common operations in time complexity O(sqrt(N)). The idea of t...