Monday, 13 January 2020
Autoscaling an EKS Cluster with Cluster Autoscaler
Last time we introduced how to use ``eksctl`` to create an EKS cluster. If you miss the previous post, please check out [Creating an EKS Cluster in AWS Using eksctl](https://dev.to/wingkwong/creating-an-eks-cluster-in-aws-using-eksctl-10ik). In this article, you will learn how to autoscale an EKS cluster using a default Kubernetes component - [Cluster Autoscaler](https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/tree/master/cluster-autoscaler). It can be used to scale either pods or nodes in a cluster and automatically increases the size of an auto-scaling group.
Go to AWS console and navigate to EC2 Dashboard - Auto Scaling Groups.
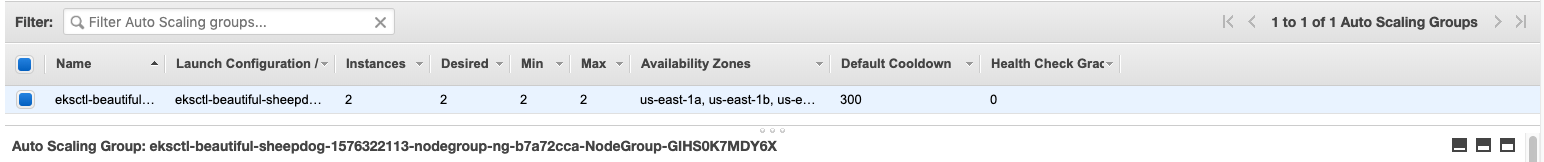
Copy the auto-scaling group name and replace ```` with it.
With ``--nodes=2:8``, it will auto-scale with minimum 2 nodes and maximum 8 nodes.
cluster_autoscaler.yaml
```
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events","endpoints"]
verbs: ["create", "patch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/eviction"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/status"]
verbs: ["update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
resourceNames: ["cluster-autoscaler"]
verbs: ["get","update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get","update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods","services","replicationcontrollers","persistentvolumeclaims","persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["replicasets","daemonsets"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get"]
- apiGroups: ["policy"]
resources: ["poddisruptionbudgets"]
verbs: ["watch","list"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["statefulsets"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["watch","list","get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["cluster-autoscaler-status"]
verbs: ["delete","get","update"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-autoscaler
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-addon: cluster-autoscaler.addons.k8s.io
k8s-app: cluster-autoscaler
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: cluster-autoscaler
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler
namespace: kube-system
labels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cluster-autoscaler
spec:
serviceAccountName: cluster-autoscaler
containers:
- image: k8s.gcr.io/cluster-autoscaler:v1.2.2
name: cluster-autoscaler
resources:
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 300Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 300Mi
command:
- ./cluster-autoscaler
- --v=4
- --stderrthreshold=info
- --cloud-provider=aws
- --skip-nodes-with-local-storage=false
- --nodes=2:8:
env:
- name: AWS_REGION
value: us-east-1
volumeMounts:
- name: ssl-certs
mountPath: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
readOnly: true
imagePullPolicy: "Always"
volumes:
- name: ssl-certs
hostPath:
path: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt"
```
Then we need to apply below inline IAM policy to worker nodes to allow them to manipulate auto-scaling
```json
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups",
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingInstances",
"autoscaling:DescribeTags",
"autoscaling:SetDesiredCapacity",
"autoscaling:TerminateInstanceInAutoScalingGroup"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
```
Go back to AWS Console - IAM and search the worker node group role created by eksctl
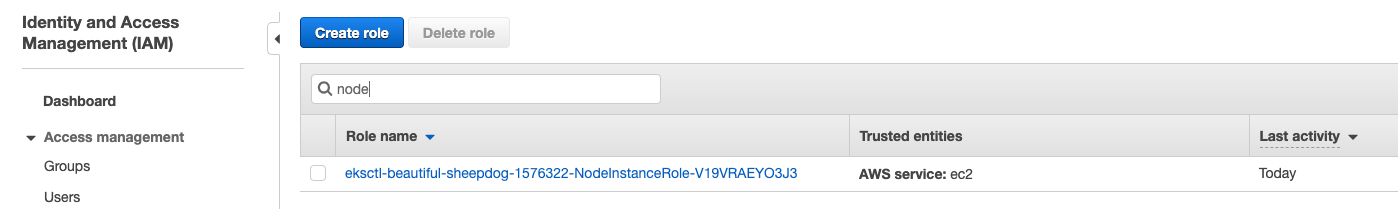
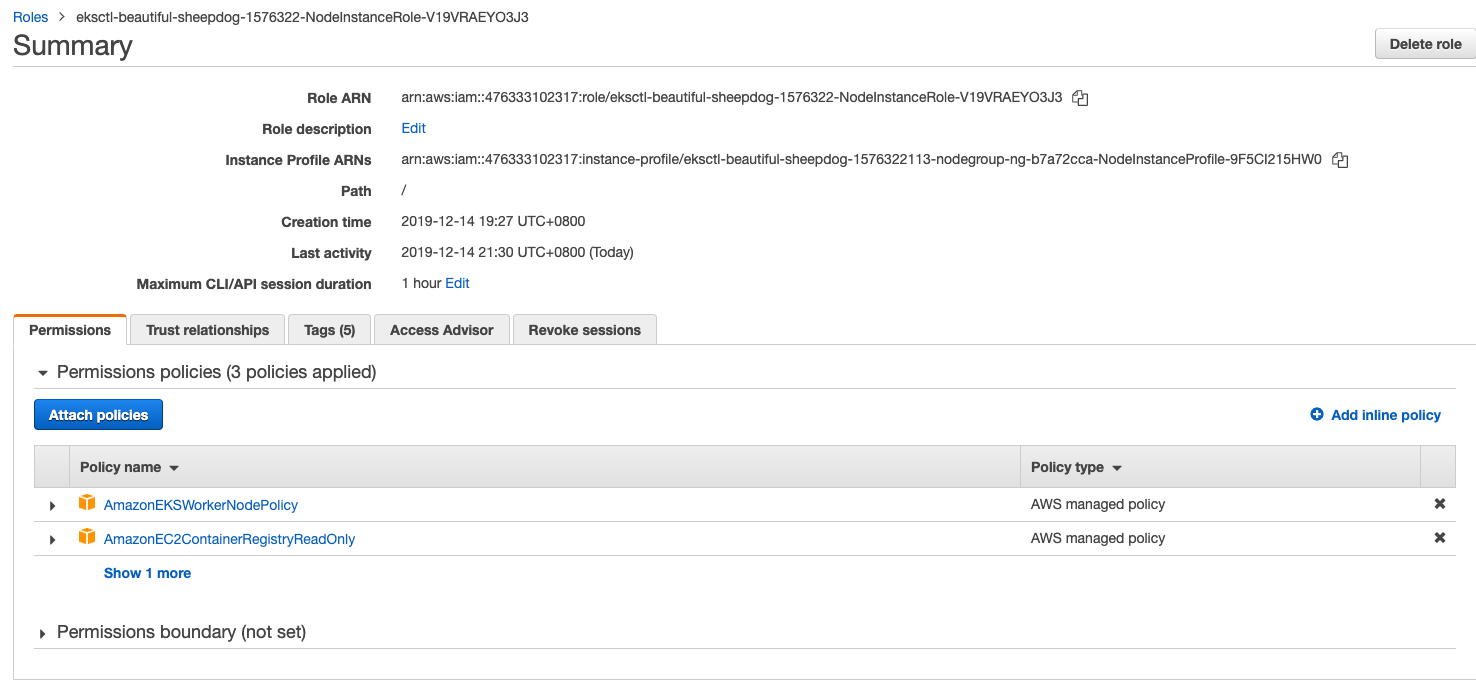
Click Add inline poilcy
Click JSON tab and paste the above policy
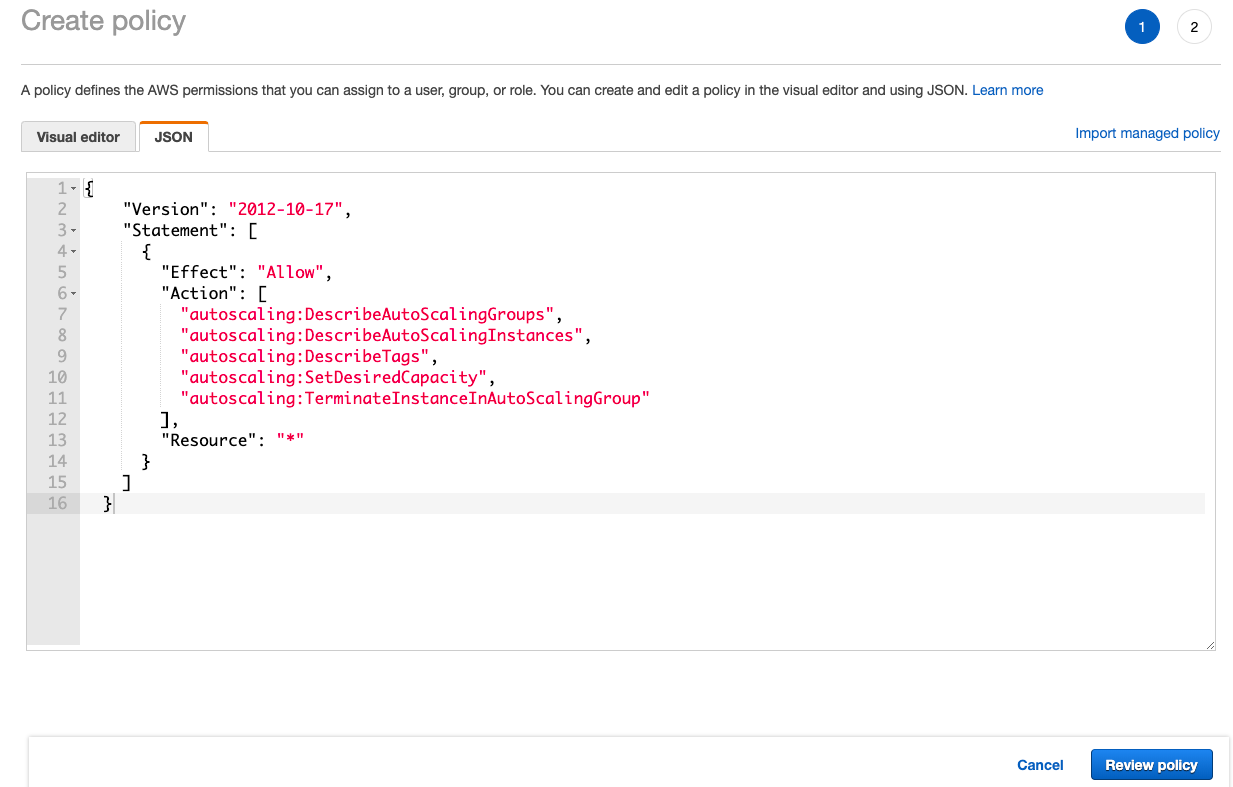
Name the policy and click Create policy
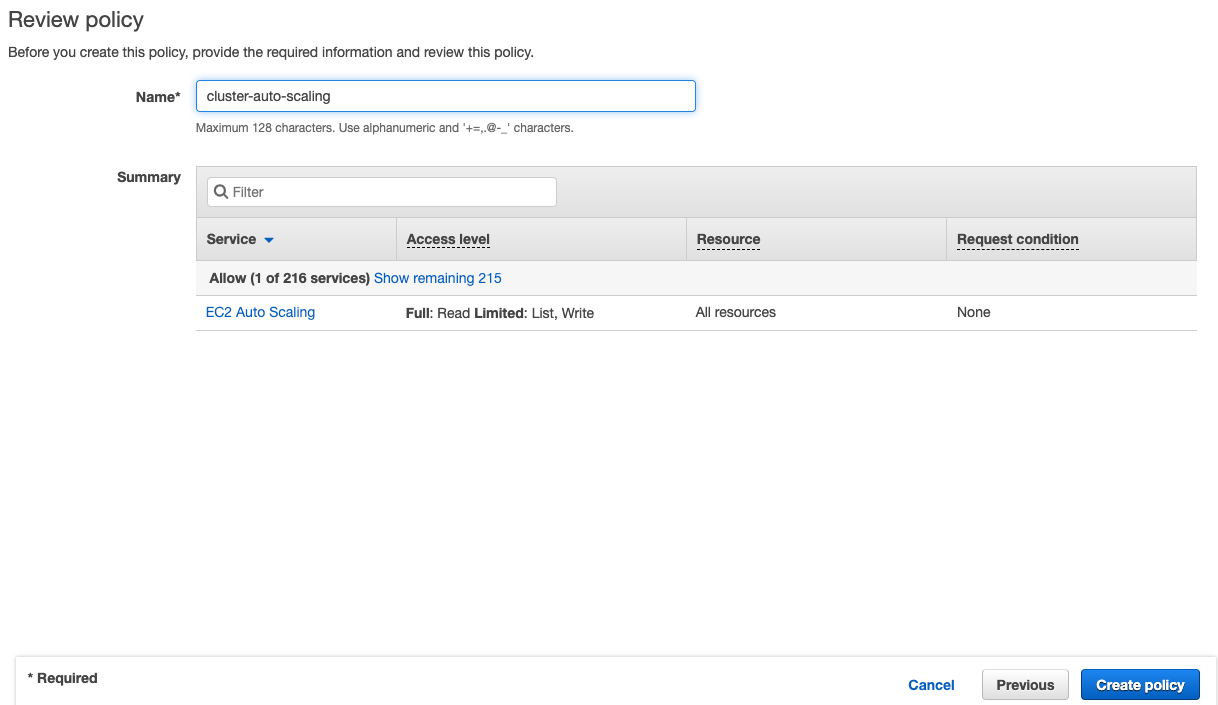
Run ``kubectl apply`` to deploy the autoscaler
```
kubectl apply -f cluster_autoscaler.yaml
```
You should see the following
```
serviceaccount/cluster-autoscaler created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-autoscaler created
deployment.extensions/cluster-autoscaler created
```
Then let's deploy an Nginx sample application
```
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-scaleout
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
service: nginx
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx-scaleout
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
```
```
kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
```
Check the deployment
```
kubectl get deployment/nginx-scaleout
```
```
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-scaleout 1/1 1 1 14s
```
Let's scale the deployment with 10 replicas
```
kubectl scale --replicas=10 deployment/nginx-scaleout
```
```
deployment.extensions/nginx-scaleout scaled
```
You can run the following to see how it goes
```
kubectl logs -f deployment/cluster-autoscaler -n kube-system
```
Let's run it again
```
kubectl get deployment/nginx-scaleout
```
You can see 10 replicas have been scaled out
```
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-scaleout 10/10 10 10 5m
```
Go to AWS Console - EC2 Dashboard. You should see there are 2 more instances spinning up.
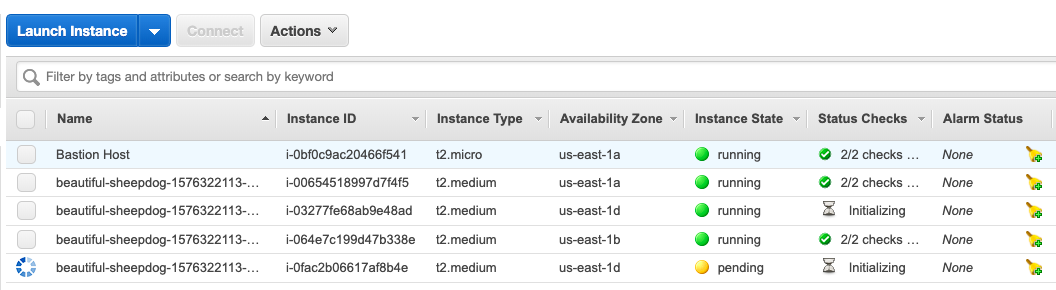
After a few minutes, try to see the nodes
```
kubectl get nodes
```
You'll get two more nodes joining to the cluster.
```
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-28-185.ec2.internal Ready 174m v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
ip-192-168-33-53.ec2.internal Ready 174m v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
ip-192-168-64-112.ec2.internal Ready 87s v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
ip-192-168-90-156.ec2.internal Ready 2m5s v1.14.7-eks-1861c5
```
To delete the deployments, run the following commands
```
kubectl delete -f cluster_autoscaler.yaml
kubectl delete -f nginx.yaml
```
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
A Fun Problem - Math
# Problem Statement JATC's math teacher always gives the class some interesting math problems so that they don't get bored. Today t...
-
SHA stands for Secure Hashing Algorithm and 2 is just a version number. SHA-2 revises the construction and the big-length of the signature f...
-
## SQRT Decomposition Square Root Decomposition is an technique optimizating common operations in time complexity O(sqrt(N)). The idea of t...
No comments:
Post a Comment